

This whole process in some species can take only 15 minutes. Each cell now has everything it needs to continue life’s functions independently. The final step includes breaking down any additional proteins or other molecules that still connect the two cells. Finally, as seen in step 5, the cells separate from each other as a new bacterial cell wall forms. As the cell lengthens in preparation for division, DNA molecules are carried to different sides of the cell.Ī cleavage groove appears in the cell membrane, as the cell wall and membrane begin to pinch and create two new cells. Individual copies of DNA adhere to different parts of the cell membrane. Thus, two new chromosomes with genetic load identity from the same stem cell and the growth of the cell occur.īoth DNA and plasmids have been duplicated. Which separate at each end of the chromosome until they come off. Therefore, when the genetic material has already been duplicated and proceeds to separate, it creates two new origins. It is where the process of binary fission begins on this chromosome, which inside contains the element of origin of replication, where the DNA is duplicated.
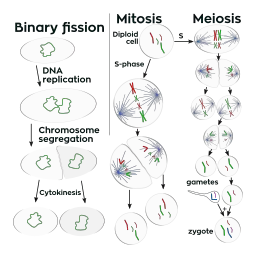
Which in turn contains a single chromosome that contains all the genetic information of the living being. As we know prokaryotic cell does not have a nucleus, therefore genetic information or DNA is located in the area called nucleoid. The fact that binary fission is carried out in the prokaryotic cells makes it a simple and fast method due to its varied characteristics. apart from that this is the reason for the great evolutionary success of bacteria, present in absolutely the whole world. This produces new bacterial strains better adapted to the environment (for example, more resistant to antibiotics). In addition to rapid colonization of the environment, this reproductive rhythm has adaptive purposes: with that reproductive rhythm, the rate of mutations is usually high. In some species, it can occur at an impressive rate (an Escherichia coli bacterium can divide once every 20 minutes), as long as the conditions of the surrounding environment are adequate. This is the most common form of reproduction in the bacterial world. It consists of the duplication of the individual’s cellular DNA, as a previous step to the division of the cytoplasm Thus, it produces two daughter cells with identical genetic material. The bipartition or binary fission is a mechanism of asexual reproduction of single-celled living beings, typical of prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea. It is a process used by bacteria and other organisms to carry out cell division which is completed in different steps. It is characterized by a very fast process in some organisms, so its growth can become exponential. Where two new completely identical living beings are formed. Binary fission also known as bipartition, is one of the types of asexual reproduction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
